[1. Introduction]
- transductive learning: node & edge가 training~prediction phase에서 그대로 남아있음 (access 가능). unseen node와 edge 처리 못함
- inductive learning: 그래프 일부에서만 학습하고, 그 모델을 unseen node or deges를 예측하는 데 사용
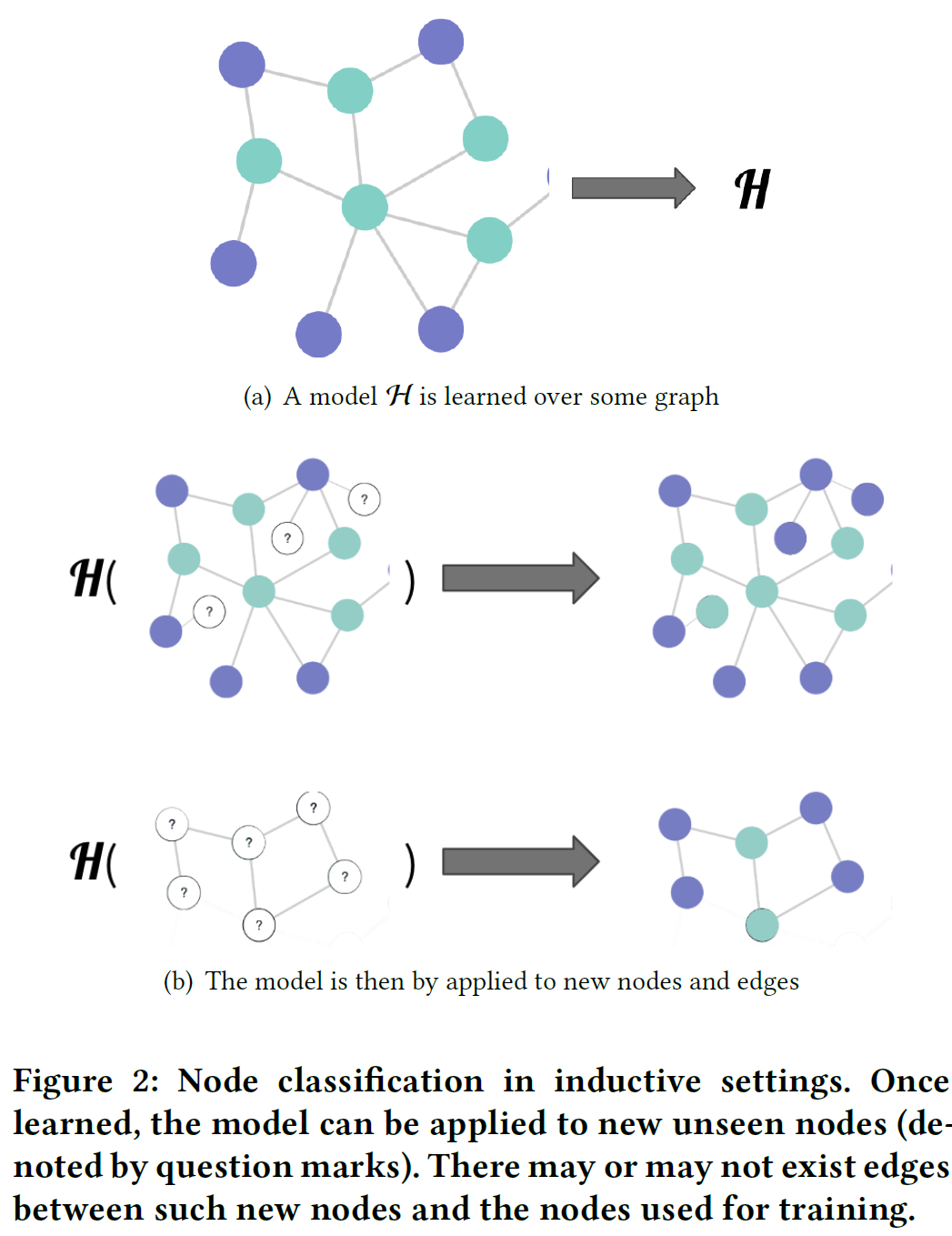
- Paradigm: spectral architecture on undirected graph in transductive settings → spatial ones that can apply inductively to arbitrary graphs
{contribution}
- discuss some theoretical tools to better visualize the operations performed by spatial GNNs
- analyze the inner workings of the SOTA spatial architecture,s specifically aggregation-based GNNs
- propose simple technique: Node masking
[2. A brief history of GNNs]
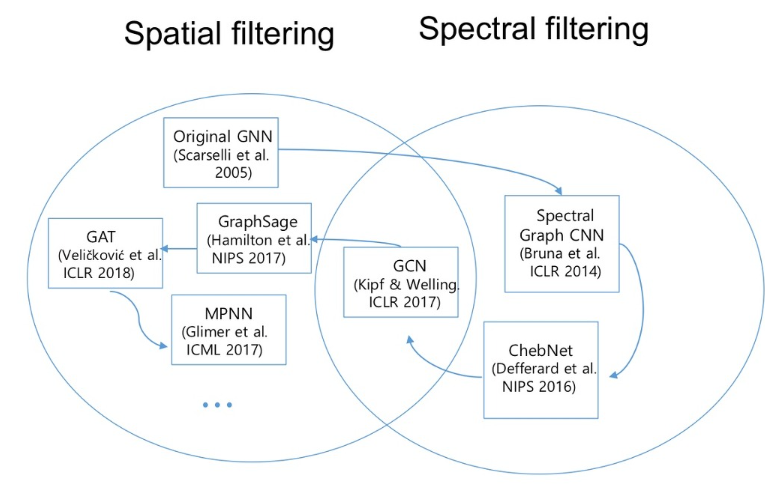
[2.1 Spectral GNNs] - message passing
- learns spectral filters regard to Laplcian → lack of scalibility
- ChebNet, GCN
[2.2 Spatial GNNs]
- defines the convolution operation directly on the structure of the graph
- sampling-based: GraphSAGE
- aggregation-based(Generally SOTA): GAT, GIN(maximally powerful)
[4. Analysis of Aggreagation-based GNNs]

[5. Node masking]
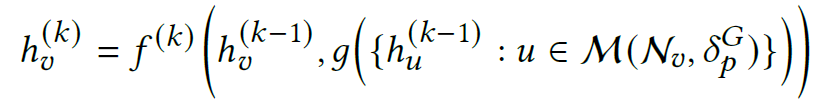
- node masking of GAT and GIN (respectively)
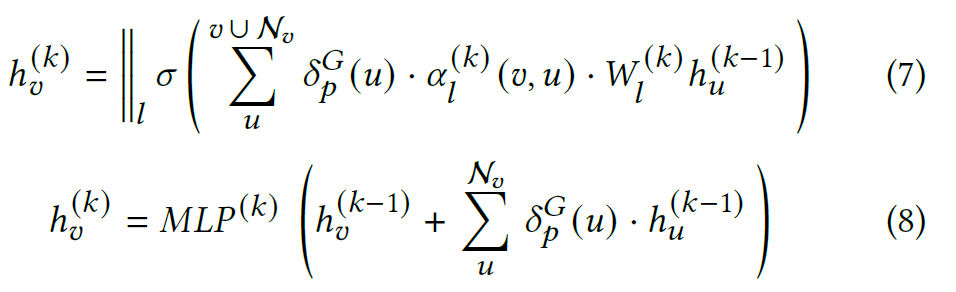
[5.2 Node masking vs Dropout techniques]
- dropedge: randomly drops a subset of edges from the graph in every training epoch
- in our experiment, node masking이 dropedge보다 효과 좋음
[6.3 Experimental setting]
- pytorch, 2-layer GIN
- simple GAT (SGAT)
- if node mask active → in every training epoch, randomly sample a Bernolli select function over the nodes in the training set
- transductive- make entire graph
- inductive- make avalibale at training time the graph G formed by nodes in the train set + edges among them