[Abstract]
- compare predictor
- curve extrapolation
- weight sharing
- supervised learning
- zero-cost proxies
- test correlation- rank-based performance measures
[Introduction]
- contributions
- the first large-scale study of performance predictors
- release comprehensive library of 31 performance predictors
- combining different families of performance predictors → better predictive power
[2. Related work]
- NAS
- initial: RL, EL, one-shot, predictor-based
- recent: tree-based methods
[3. Performance prediction methods for NAS]
- goal: find a model with smallest validation error
- due to computational cost, introduce performance predictor f’ which is aligned with f (validation error)
- performance predictor
- initialize routine: first time
- query routine: many time
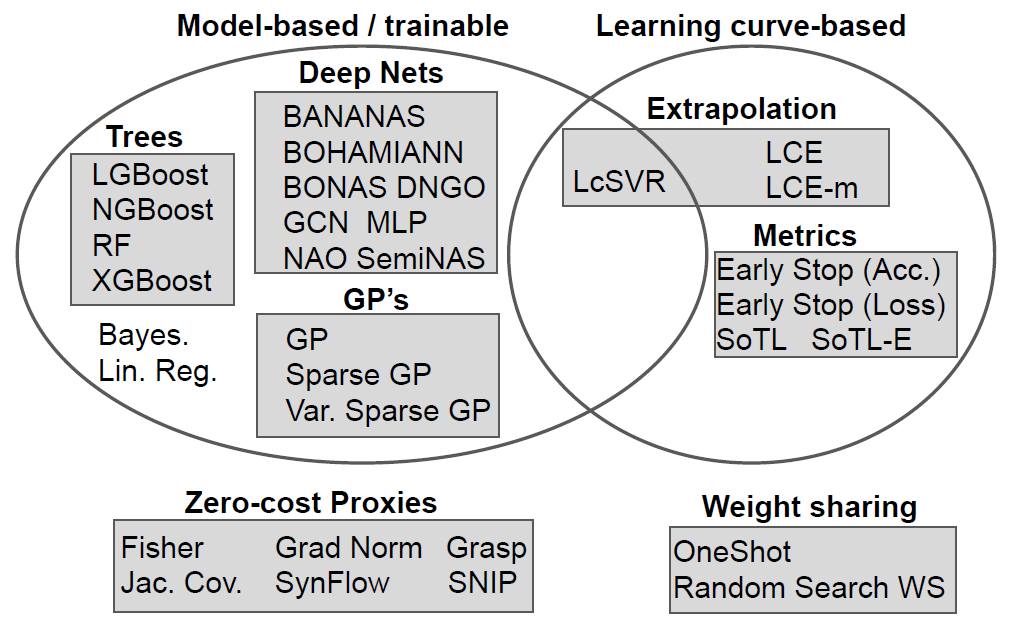
- model-based (trainable) methods
- most common
- initialization routine: fully training many architectures
- query time: less than a second
- framework: BO, evolutionary, tree-based
- learning curve-based methods
- partially trained network, extrapolating the learning curve
- doesn’t require initialization time
- query time takes minutes
- hybrid methods
- curve + model-basd methods
- zero-cost methods
- initialize
- weight sharing methods
- all architeuctures in the search space are combined to form a single over-parameterized supernetwork
- not effective at ranking
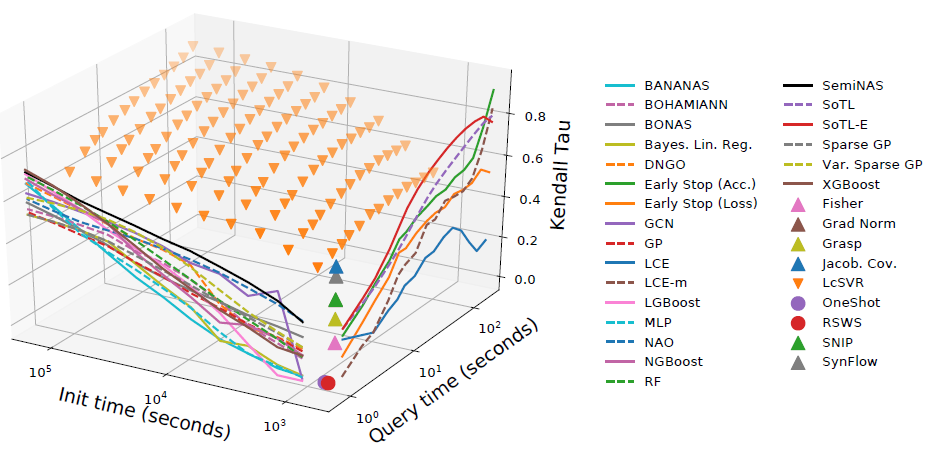
- tradeoff between initialize and query time
- different model requires different initialize / query time
[4. Experiments]
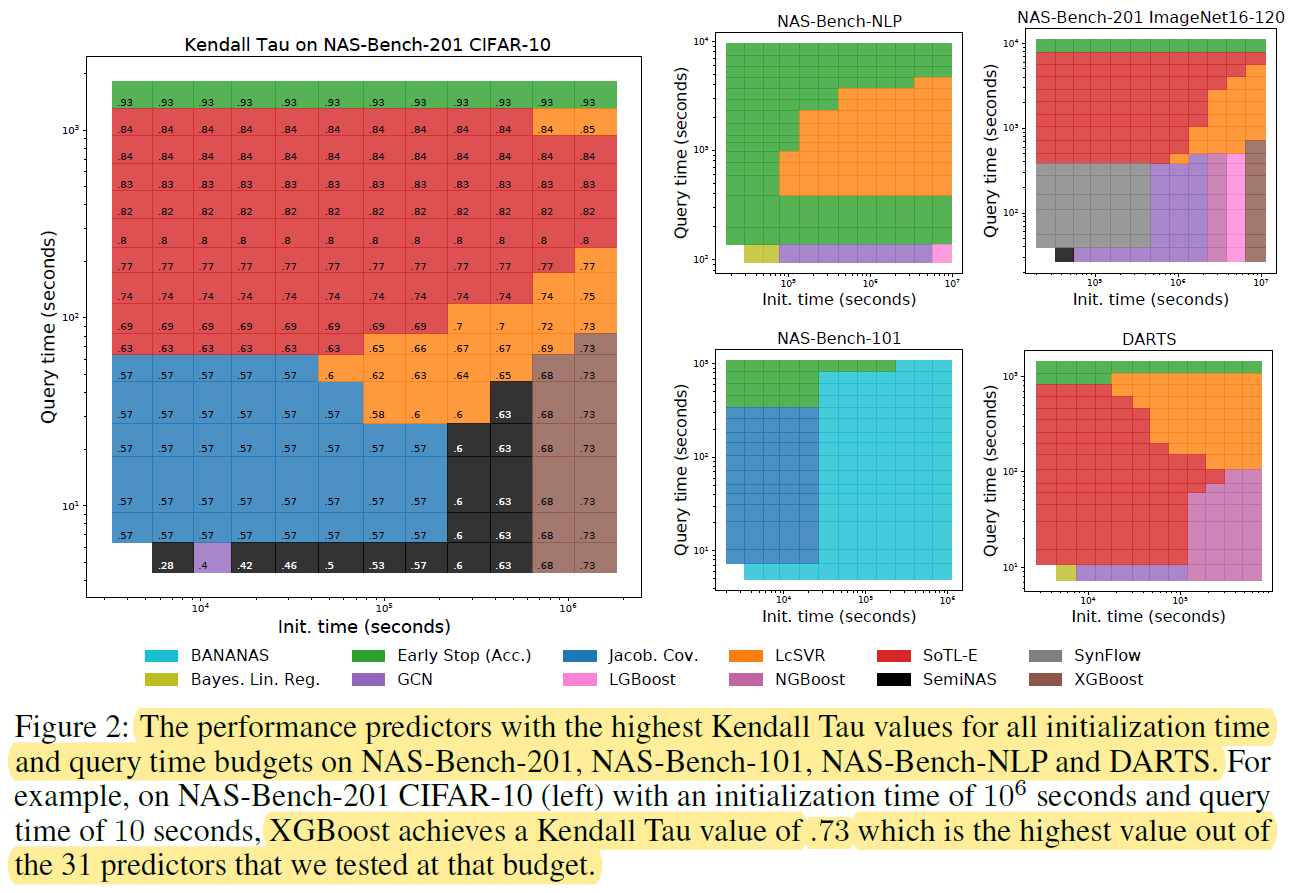
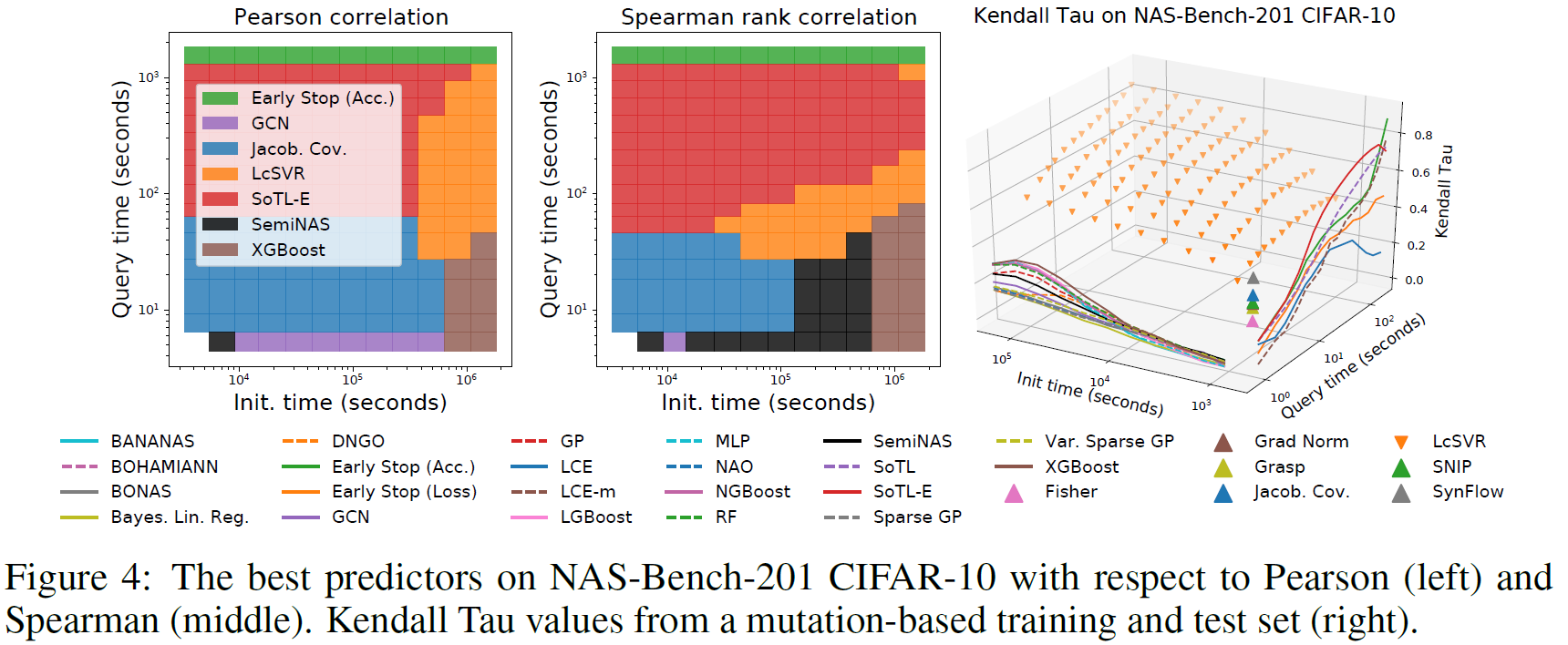
- NAS benchmark datasets
- NAS-Bench-101
- NAS-Bench-201
- DARTS search space : 1e18
- NAS-Bench-301
- NAS-Bench-NLP: 1e53